How Low Can They Go?
How low can natural gas prices go? We may find out soon. First some background.
US natural gas demand varies considerably over the course of a year, driven primarily by natural gas usage related to heating. During peak winter months, natural gas demand exceeds the production capacity of North American natural gas wells. Natural gas can be stored underground in significant quantities in depleted reservoir, salt cavern, and aquifer storage facilities and called upon to meet demand during these peak winter usage periods.
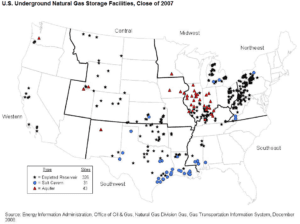
The US underground natural gas storage infrastructure is extensive, as shown on the above map.
Natural gas is injected into underground storage facilities during periods of low demand and then withdrawn during times of peak demand. As natural gas is injected and withdrawn from these storage facilities, some natural gas must remain in the reservoir in order to maintain adequate pressure. This is referred to as “base” or “cushion” gas and is permanent inventory. Additional natural gas in an underground storage facility is “working” gas and is available to be delivered during higher demand periods.
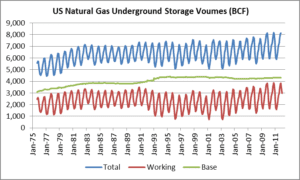
The graph above shows monthly US natural gas base, working, and total storage volumes going back to September 1975. The injection and withdrawal of working gas is highly seasonal (red line) while base gas levels are much more stable (green line).
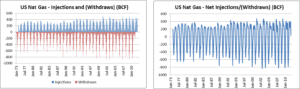
The above graphs show monthly US natural gas injections and withdrawals (gross and net), over the same 436 month time period. Both graphs are asymmetric along the horizontal zero axis. Over time, injections equal withdrawals. However, working gas is injected more evenly during non-winter time periods while withdraws occur much more quickly during the winter.
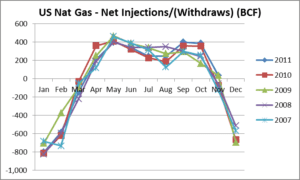
As shown on the above graph, natural gas is generally injected during the months of April through October and withdrawn heavily during December, January, and February.
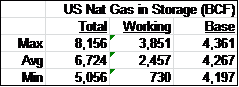
Looking back over the past ten years, as shown in the table above, the US natural gas base gas level has remained fairly steady at about 4,300 billion cubic feet (BCF) while monthly working gas has varied considerably from a low of 730 BCF to a high of 3,851 BCF.
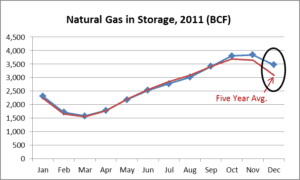
More recently, the US ended the year 2011 with 3,472 BCF of working gas in storage, 12.5% above the 3,087 BCF year-end average of the past five years.
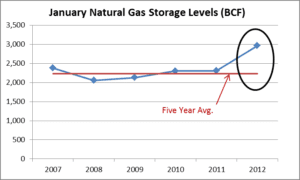
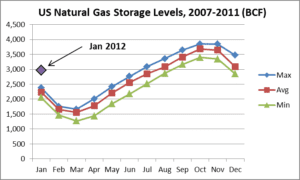
At month end, January 2012, the US natural gas storage level stood at 2,966 BCF, 729 BCF (or more than 30%) higher than the five year January average of 2,237 BCF. This is significant.
Much lower than normal volumes of natural gas have been withdrawn from storage as a result of the mild winter so far, and the large amount of natural gas in storage represents a significant overhang of supply as the winter heating season winds down. What does this mean for natural gas prices in the near term? Unless February and March are exceptionally cold, short term natural gas prices are headed down.
Spot natural gas prices could be headed to sub $2 per million Btu (mmBtu) or even sub $1 per mmBtu levels. Liam Denning, writing in the The Wall Street Journal, recently suggested that spot natural gas prices could turn NEGATIVE. How can this be?
For operational reasons, natural gas storage reservoirs must be cycled. Working gas can be injected under pressure and stored for several months, but the natural gas must be periodically removed in order to reduce reservoir pressure and maintain the integrity of the storage reservoir. Storage operators levy stiff penalties if storage customers do not adhere to withdrawal schedules. Normally, this is not an issue for storage customers as their natural gas is withdrawn during the winter heating season. But at this point, it does not look like there is enough winter left for end users to need the large volume of natural gas in storage. And, the gas cannot stay in storage until next winter because the reservoirs need to be cycled down. So, in order to avoid penalties, storage customers may have to liquidate their positions during the spring when demand for natural gas is generally at its lowest, or during the summer time. This would drive spot market prices down. It is conceivable that prices could get down to zero, at which point storage customers may be motivated to pay someone to take their gas in order to avoid penalties.
The Avalon Advantage – Visit our website at www.avalonenergy.us, call us at 888-484-8096, or email us at jmcdonnell@avalonenergy.us.
Copyright 2012 by Avalon Energy® Services LLC
